September 2021- August 2023
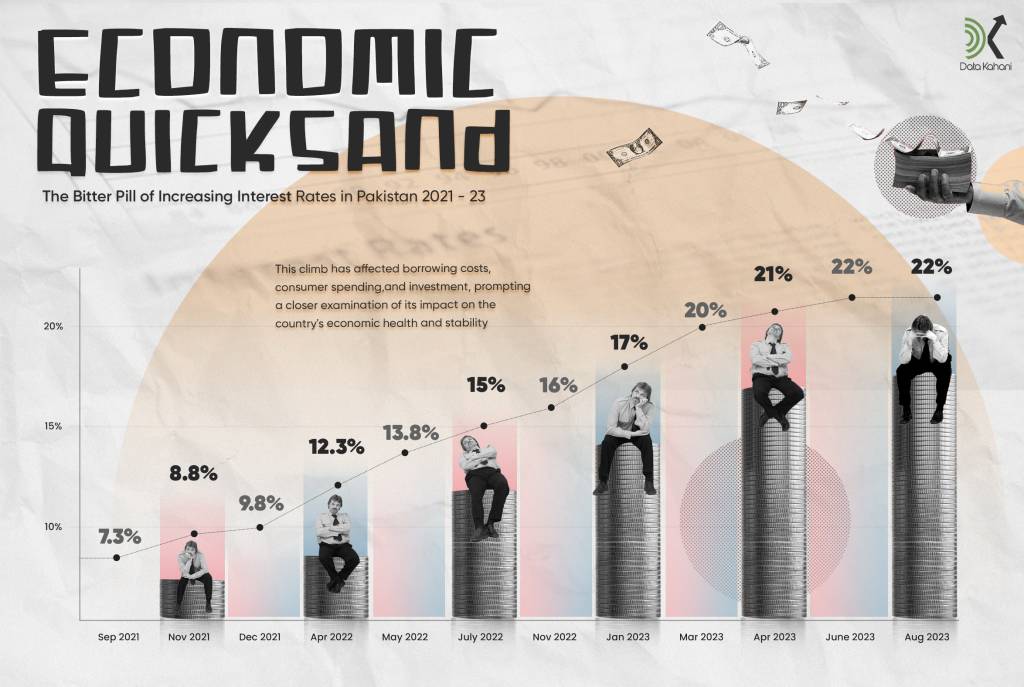
Over the course of almost two years, Pakistan’s economy has been navigating a significant and sustained increase in interest rates, a phenomenon that holds far-reaching implications for the nation’s economic landscape. Beginning in September 2021 and extending through August 2023, this period of escalating interest rates has set the stage for several intricate changes within the country’s financial dynamics.
The Economic Context
The decision to raise interest rates is often a complex one, driven by various factors including inflation, monetary policy, and the broader economic climate. Central banks use interest rates as a tool to manage economic growth, inflation, and currency stability. In the case of Pakistan, this upward shift reflects an attempt to curb inflation and stabilize the currency amidst global economic uncertainties.
Impact on Borrowing and Investments
The most immediate impact of increasing interest rates is felt by borrowers. This includes both individuals and businesses seeking loans. As interest rates rise, borrowing becomes more expensive, discouraging people from taking out loans or increasing their existing debts. Businesses that rely on borrowing to finance operations or expansion may experience a slowdown due to the higher cost of capital. This, in turn, could lead to reduced investment and potentially impact job creation.
Consumer Behavior and Spending
Higher interest rates also affect consumer behavior. When borrowing becomes costlier, individuals may rethink discretionary spending on big-ticket items like cars and homes. Major purchases that often require loans become less appealing, as the cost of borrowing rises. Consequently, sectors like real estate and automobile sales could experience a downturn.
Impact on the Stock Market
The stock market is another area sensitive to interest rate fluctuations. As interest rates rise, borrowing costs increase for companies, which could potentially lower their profits. This might lead to decreased investor confidence and a decline in stock prices.
Exchange Rate and Trade Balance
Interest rate differentials between countries can impact exchange rates. If a country’s interest rates rise significantly compared to those of its trading partners, its currency could appreciate. While this could benefit imports by making them cheaper, it could negatively impact exports as foreign buyers find the country’s products more expensive.
Government Debt and Fiscal Policy
Higher interest rates also affect the government’s borrowing costs. Governments often issue bonds to raise funds, and the interest they pay on these bonds rises with market interest rates. This could increase government expenditures on servicing the debt, potentially impacting fiscal policies and the budget.
The continuous increase in interest rates from September 2021 to August 2023 has engendered a complex web of effects on Pakistan’s economy. From the borrowing patterns of individuals and businesses to investment decisions, consumer behavior, stock market performance, and the nation’s trade balance, each facet of the economy is interwoven with the trajectory of these interest rate hikes. As the country continues to navigate these shifts, policymakers and economic experts face the intricate challenge of maintaining a balance between curbing inflation, fostering economic growth, and ensuring overall stability.



